Carotid Artery Disease
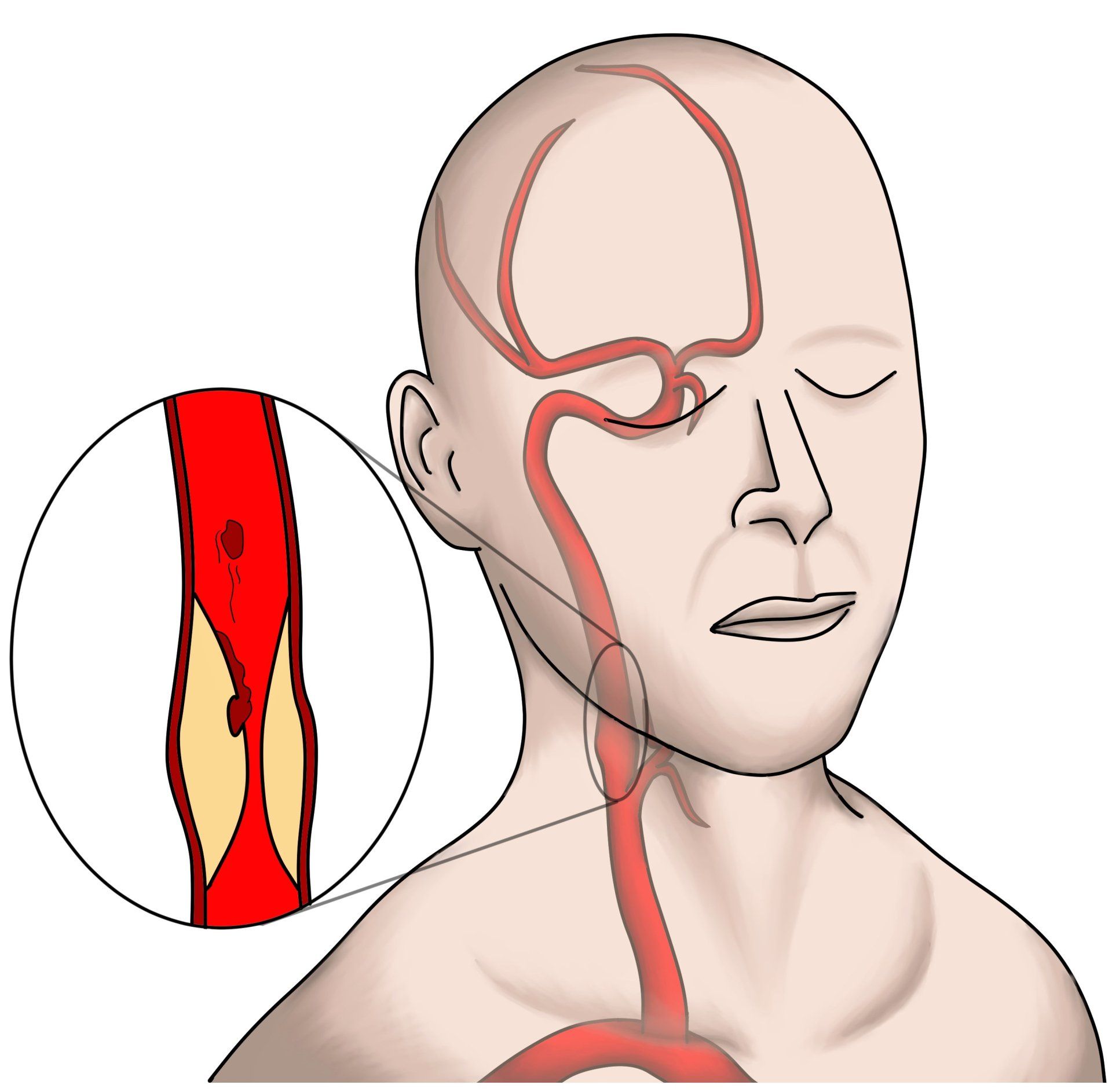
Carotid Artery Disease/Cerebrovascular disease is narrowing (almost always from plaque build-up) in the arteries leading to the brain. The plaque that builds up in your arteries consists of cholesterol, calcium, and fat. It is almost always associated with smoking and diabetes. Other risk factors include high blood pressure (hypertension), high cholesterol, family history (genetics), obesity, end stage renal disease, and lack of exercise.
The Carotid artery in the neck is the source of blood to your brain and therefore a narrowing or blockage in the carotid artery can lead to a debilitating stroke.
Symptoms
- Unfortunately, most people don't have any symptoms until they develop a stroke, so it's important to be screened for carotid artery disease.
- If symptoms of carotid artery occur, they may include sudden arm or leg numbness or weakness, facial droop, difficulty with speech (slurring or word finding difficulty), difficulty understanding speech, or temporary one sided blindness.
Diagnosis
- Often found on a screening carotid ultrasound examination like Life Line Screening.
- An exam by your family physician or vascular surgeon may consist of a good history, including risk factors and family history as well as a physical exam.
- Based on the exam by your doctor, a carotid ultrasound may be ordered.
- If the carotid ultrasound in abnormal, a carotid CT scan may be performed.
Treatment
- Non surgical. This would include controlling the blood pressure with medications, lowering the cholesterol or lipids with diet and medications, stop smoking cigarettes, and exercise.
- Treatment may be indicated for a greater than 70% narrowing in the internal carotid artery even if no symptoms are present. If symptoms occur, the carotid artery is usually treated if the stenosis is greater than 50%. Endovascular carotid artery stent may be recommended if not a candidate for carotid endarterectomy. Carotid surgery (Carotid Endarterectomy) is a procedure where the plaque is surgically removed from the carotid artery in the operating room.